- Ethical Hacking Statement
- The Modern Security Operations Center
- The Windows Operating System
- Linux Basics
- Network Protocols
- Ethernet and IP Protocol
- Connectivity Verification
- Address Resolution Protocol
- The Transport Layer
- Network Services
- Network Communication Devices
- Network Security Infrastructure
- Attackers and Their Tools
- Common Threats and Attacks
- Network Monitoring and Tools
- Attacking the Foundation
- Attacking What We Do
- Understanding Defense
- Access Control
- Threat Intelligence
- Public Key Cryptography
- EndPoint Protection
- Endpoint Vulnerability
- Technologies and Protocols
- Network Security Data
- Evaluating Alerts
- Working with Network Security Data
- Digital Forensics and Incidents Analysis and response
1. What are two roles of the transport layer in data communication on a network? (Choose two.)
- A. Providing frame delimiting to identify bits making up a frame
- B. Tracking the individual communication between applications on the source and destination hosts
- C. Providing the interface between applications and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted
- D. Performing a cyclic redundancy check on the frame for errors
- E. Identifying the proper application for each communication stream
The transport layer has several responsibilities. The primary responsibilities include
the following:
Tracking the individual communication streams between applications on the source and
destination hosts
Segmenting data at the source and reassembling the data at the destination
Identifying the proper application for each communication stream through the use of port
numbers
2. During a TCP session, a destination device sends an acknowledgment number to the source device. What does the acknowledgment number represent?
- A. The next byte that the destination expects to receive
- B. One number more than the sequence number
- C. The last sequence number that was sent by the source
- D. The total number of bytes that have been received
The window size determines the number of bytes that will be sent before expecting
an acknowledgement. The acknowledgement number is the number of the next expected byte.
For example, if a host has received 3140 bytes, the host would respond with an
acknowledgement number of 3141.
3. Which two services or protocols use the preferred UDP protocol for fast transmission and low overhead? (Choose two)
- A. HTTP
- B. FTP
- C. VoIP
- D. POP3
- E. DNS
Both DNS and VoIP use UDP to provide low overhead services within a network
implementation.
4. Which transport layer feature is used to guarantee session establishment?
- A. UDP sequence number
- B. UDP ACK flag
- C. TCP port number
- D. TCP 3-way handshake
TCP uses the 3-way handshake. UDP does not use this feature. The 3-way
handshake ensures there is connectivity between the source and destination devices before transmission occurs.
5. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function of TCP or UDP in this situation? (Choose three.)
- A. TCP is the preferred protocol when a function requires lower network overhead.
- B. The source port field identifies the running application or service that will handle data returning to the PC.
- C. The TCP source port number identifies the sending host on the network.
- D. UDP segments are encapsulated within IP packets for transport across the network.
- E. The UDP destination port number identifies the application or service on the server which will handle the data.
- F. The TCP process running on the PC randomly selects the destination port when establishing a session with the server.
Layer 4 port numbers identify the application or service which will handle the data.The source port number is added by the sending device and will be the destination port number when the requested information is returned. Layer 4 segments are encapsulated within IP packets. UDP, not TCP, is used when low overhead is needed. A source IP address, not a TCP source port number, identifies the sending host on the network. Destination port numbers are specific ports that a server application or service monitors for requests.
6. What is the purpose of the TCP sliding window?
- A. To request that a source decrease the rate at which it transmits data
- B. To end communication when data transmission is complete
- C. To inform a source to retransmit data from a specific point forward
- D. To ensure that segments arrive in order at the destination
The TCP sliding window allows a destination device to inform a source to slow
down the rate of transmission. To do this, the destination device reduces the value contained in the window field of the segment. It is acknowledgment numbers that are used to specify retransmission from a specific point forward. It is sequence numbers that are used to ensure segments arrive in order. Finally, it is a FIN control bit that is used to end a communication session.
7. What is the purpose of the TCP sliding window?
- A. The part of the FTP message that was lost is re-sent.
- B. The message is lost because FTP does not use a reliable delivery method.
- C. The FTP source host sends a query to the destination host.
- D. The entire FTP message is re-sent.
Because FTP uses TCP as its transport layer protocol, sequence and acknowledgment numbers will identify the missing segments, which will be re-sent to complete the message.
8. Which two flags in the TCP header are used in a TCP three-way handshake to establish connectivity between two network devices? (Choose two.)
- A. FIN
- B. SYN
- C. RST
- D. URG
- E. PSH
- F. ACK
TCP uses the SYN and ACK flags in order to establish connectivity between two
network devices.
9. Which tool is used to provide a list of open ports on network devices?
- A. Tracert
- B. Ping
- C. Whois
- D. Nmap
The Nmap tool is a port scanner that is used to determine which ports are open on a
particular network device. A port scanner is used before launching an attack.
10. Which two fields are included in the TCP header but not in the UDP header? (Choose two.)
- A. Source port
- B. Sequence number
- C. Checksum
- D. Window
- E. Destination port
The sequence number and window fields are included in the TCP header but not in
the UDP header.
11. Refer to the exhibit. Which three lines represent the TCP three-way handshake?
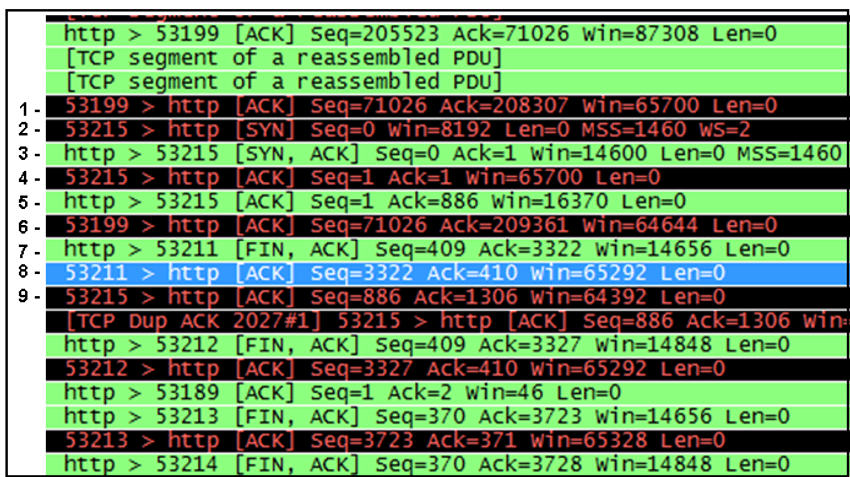
- A. Lines 2, 8, and 9
- B. Lines 2, 3, and 4
- C. Lines 1, 2, and 3
- D. Lines 4, 5, and 6
- E. Lines 6, 7, and 8
A three-way handshake is recognizable by the SYN flag being set first, then the
SYN, ACK response, followed by the final ACK flag being sent in a packet.
12. What is a characteristic of a TCP server process?
- A. Every application process running on the server has to be configured to use a dynamic port number.
- B. A host running two different applications can have both configured to use the same server port.
- C. There can be many ports open simultaneously on a server, one for each active server application.
- D. An individual server can have two services assigned to the same port number within the same transport layer services.
Each application process running on the server is configured to use a port number,
either by default or manually, by a system administrator. An individual server cannot have two services assigned to the same port number within the same transport layer services. A host running a web server application and a file transfer application cannot have both configured to use the same server port. There can be many ports open simultaneously on a server, one for each active server application.
