- Basic Networking Interview Questions
- Networking Interview Questions
- Network Firewall Interview Questions
- CCNA Interview Questions [1]
- CCNA Interview Questions [2]
- CCNA Interview Questions [3]
- CCNA Interview Questions [4]
- CCNA Interview Questions [5]
- CCNA Interview Questions [6]
- CCNA Interview Questions [7]
- CCNA Interview Questions [8]
- CCNA Interview Questions [9]
- CCNA Interview Questions [10]
- CCNA Interview Questions [11]
- CCNA Interview Questions [12]
- CCNA Interview Questions [13]
- CCNA Interview Questions [14]
- CCNA Interview Questions [15]
- CCNA Interview Questions [16]
- OSPF Interview Questions
- BGP Interview Questions
- Linux Interview Question [1]
- Windows Server Interview Questions [1]
- Windows Server Interview Questions [2]
- Windows Server Interview Questions [3]
- Windows Server Interview Questions[4]
- SQL Interview Questions [1]
- SQL Server Interview Question [3]
- VMware vSphere 7.0: ICM Interview Question
- AWS Interview Questions [1]
- AWS: Sysops Interview Questions
- Dev Ops Interview Question [1]
- OpenStack Interview Questions
- Postfix Interview Questions

Top 20+ Network Firewall Interview Questions
1. What is Network Security?
Network security is a process of securing IT infrastructure from unauthorized access, misuse, malfunction, modification, destruction, or improper disclosure. IT infrastructure includes firewalls, routers, switches, servers, and other devices, which help host the software applications. In simple terms, network security refers to all activities related to protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an organization’s software and hardware assets.
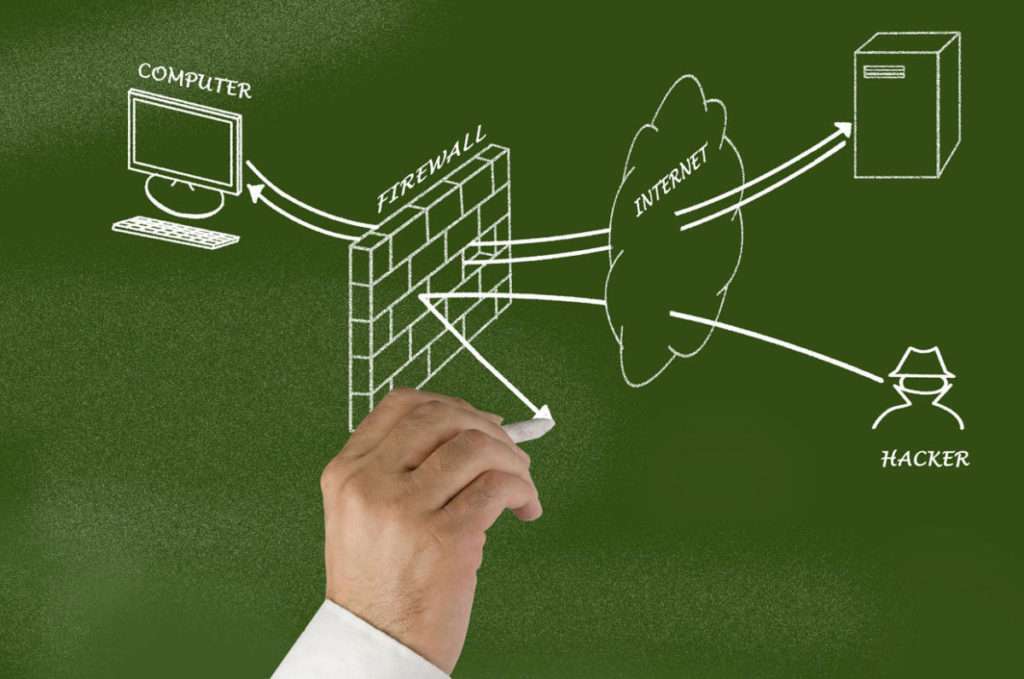
2. What is a Network Firewall?
Network firewall protects your network from unauthorized access. It filters traffic based on the configuration set by the firewall administrator. The firewall basically performs two functions, block and permit traffic based on configuration.
3. How does a firewall work?
Firewall filters network traffic based on the configuration set by the firewall administrator. It can permit or block any port number, web application, and network-layer protocols based on configuration.
Common ports:
- 80 HTTP
- 443 HTTPS
- 20 & 21 FTP
- 23 Telnet
- 22 SSH
- 25 SMTP
4. What can a firewall protect IT infrastructure inside your organization?
Firewalls are configured to protect IT infrastructure from any unauthorized access. It secures the network by implementing defined security policies, hiding and protecting your internal network addresses, and reporting threats and activities. It also provides audit logs related to network traffic to the firewall administrator, identifying the root cause of a security breach.
5. Will IPSEC make firewalls obsolete?
To discuss this question, first, we need to understand what IPSEC does? IPSEC provides host to host authentication and encryption. In simple terms, it provides a solution of integrity and confidentiality to end customers.While the firewall is protecting the network without doing encryption and host to host authentication, it monitors the traffic and permit or block based on configuration. It means we need both IPSEC and firewalls, and we can think of combining firewalls with IPSEC-enabled hosts.
6. Where does a firewall fit in the security model?
A security model is a scheme for specifying and enforcing security policies. Firewalls secure the network’s perimeters by implementing defined security policies, hiding and protecting your internal network addresses, and reporting on threats and activities.
7.What is a VPN?
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It provides a secure tunnel that protects your data from any intrusion. It is used to protect private web traffic from snooping, interference, and censorship. In simple terms, it established the connection between two private networks over the internet.
Types of VPN: Site-to-site VPN and Remote Access VPN.
8. What are the types of firewalls ?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST , an organization) from the US, divides firewalls into three basic types: Packet filters, Stateful inspection, and Proxy.
Packet filters permit or block packets based on port number, protocols source, and destination address.
Stateful inspection works on the principle of the state of active connections between client and server. It uses the state information to allow or block network traffic.
Proxy firewall combines stateful inspection technology to enable deep packet inspection. Here, the firewall act as a proxy; a client makes a connection with the firewall, and then the firewall makes a separate connection to the server on behalf of the client.
9. What is source routed traffic and why is it a threat?
Source routing is not very much used in practice. It allows a sender of a packet to partially or completely specify the route the packet takes through network.
Generally, the router decides the route from destination to source. If source-routed traffic allows through the firewall, an attacker can generate traffic claiming to be from a system “inside” the firewall. In general, such traffic wouldn’t route to the firewall properly, but with the source routing option, all the routers between the attacker’s machine and the target will return traffic along the source route’s reverse path. Implement such attacks are quite easy. Therefore it is a big threat to firewall devices.
10. What is IP Spoofing and how can it be prevented ?
IP spoofing is a practice where an attacker illicitly impersonates another machine by manipulating IP packets. There are many tools available for IP Spoofing.
It can be prevented by the following ways:
- Invest in spoofing detection software
- Implement best security practices for IT assets
- Choose reliable ISP
- Implement Cryptographic protocols such as HTTP Secure (HTTPS), Secure, etc.
- Shell (SSH) and Transport Layer Security (TLS)
- Avoid Direct IP user authentication
11. What is a Host-based Firewall?
- These are personal firewalls running on your desktops and laptops as a software.
- Firewall software is generally included in your operating system and is also available externally as a 3rd party solution.
- The main objective of the personal firewall is to stop unauthorized access to the network.
- These firewalls are generally a “Stateful” firewall and block connection based on port numbers.
- These firewalls are also used to block applications based on your configuration.
- The best example is the Windows Firewall, which works based on port number, application, and other attributes.
12. Whether a firewall is able to block some specific pages in a web application?
The answer is big Yes
- With the firewall’s help, you can allow or disallow applications such as MS SQL Server, Twitter, Facebook, and a subset of the application.
- Example: Suppose you can log in on Facebook but not post on Facebook because firewall blocks post feature on Facebook. Your firewall exactly knows what request you are sending to the Internet.
13. What are SOHO firewalls?
- It is abbreviated as Small Office/Home Office appliance. It usually provides multiple functions with many security features include a wireless access point, Router, Firewall, Content filter.
- It may not be able to provide advanced features of Dynamic Routing and Remote support.
14. What is Unified Threat Management (UTM)?
- It is also called the All-in-one security appliance and Web Security Gateway.
- These devices generally have a lot of security features such as URL filtering/content filtering, malware inspection (based on Malware signatures), spam filter, CSU/DSU built-in functionality, also act as router/switch, firewall functionality built-in, IDS/IPS capability, Bandwidth shaper may act as a VPN endpoint.
15. What is a limitation of the network firewall?
- It acts as the first line of defense against any external attack. However, it is weaponless against any internal attack.
- The firewall acts as a gatekeeper, but inside the house, it can’t stop any system harm. A firewall basically designs to protect the network from other networks.
16. What is the packet filtering firewall?
In simple words, packet filtering firewall filter traffic based on packet attributes such as source and destination addresses, source and destination port numbers, and protocol types.
17. One type of firewall is a circuit-level gateway, can you explain it?
Circuit-level gateway, as the name suggests, it allows or drops connection based on the process of creating a connection between destination and host. It involves monitoring of TCP/IP session requests between trusted hosts on the LAN and non-trusted hosts on the Internet. It verifies TCP/IP connection procedure, also called handshaking, and validity of connection.
18. Which type of firewall is more secure, packet filtering firewall or circuit-level gateway, and Why?
Circuit Level Gateway is considered more secure because Packet-filtering solutions filter traffic based on packet attributes, as discussed in the previous question. Circuit Level Gateway filters are based on the communication pattern of TCP/IP packets. Packet-filtering solutions open the system to denial-of-service (DoS) attacks (buffer overflow exploits in “allowed” applications on target machines, connections exhaustion). However, Circuit Level Gateway filters also not able to protect the system from DoS attacks completely.
19. What is the application Level gateway in the context of a network firewall?
- In this case, the firewall act as a proxy between the internal client and the external server. The main purpose of this type of firewall is to monitor and sanitize external communications.
- Whenever a user requests something from the Internet, a firewall creates another similar request and checks whether request resources do not have any malware and other security vulnerabilities.
20.What is a Stateful Inspection Firewall?
Stateful inspection is the most effective way to secure a network. It combines the features of the packet filtering firewall, Circuit Level Gateway, and Application Level gateway.
21. What are the attack methods on the network?
Some common attack methods are ping sweep, port scan, email reconnaissance, IP spoofing, DDoS attack, packet sniffing, DNS transfer, Trojan horses, backdoors, spyware, etc.
22. Explain the concept of IP spoofing.
Here, Attacker used this technique to hide actual IP. They send malicious traffic from fake IP or spoof IP. This is the challenge for security experts and law enforcement agencies to find the actual attacker. DDoS is the most popular attack by using this technique.
Subscribe us to receive more such articles updates in your email.
If you have any questions, feel free to ask in the comments section below. Nothing gives me greater joy than helping my readers!
