- CCNA Interview Questions [1]
- CCNA Interview Questions [2]
- CCNA Interview Questions [3]
- CCNA Interview Questions [4]
- CCNA Interview Questions [5]
- CCNA Interview Questions [6]
- CCNA Interview Questions [7]
- CCNA Interview Questions[8]
- CCNA Interview Questions [9]
- CCNA Interview Questions [10]
- CCNA Interview Questions [11]
- CCNA Interview Questions [12]
- CCNA Interview Questions [13]
- CCNA Interview Questions [14]
- CCNA Interview Questions [15]
- CCNA Interview Questions [16]

Top CCNA Interview Questions and Answers -4
1. Which layer specifies voltage, wire speed, and pinout cables and moves bits between devices?
Physical
2. Which layer combines bits into bytes and bytes into frames, uses MAC addressing and provide error detection?
Data Link Layer
3. Which layer is responsible for keeping the data from different applications separate on the network?
Session layer.
4. Which layer segments and resembles data into a data stream?
Transport layer
5. Which layer provides the physical transmission sof the data and handless error notification, network topology, and flow control?
Data Link Layer
6. Which Layer manages device addressing, tracks the location of devices on the network, and determine the best way to move data?
Network layer.
7. How Data breaks down on each layer from top to bottom?
Encapsulation occurs in following format 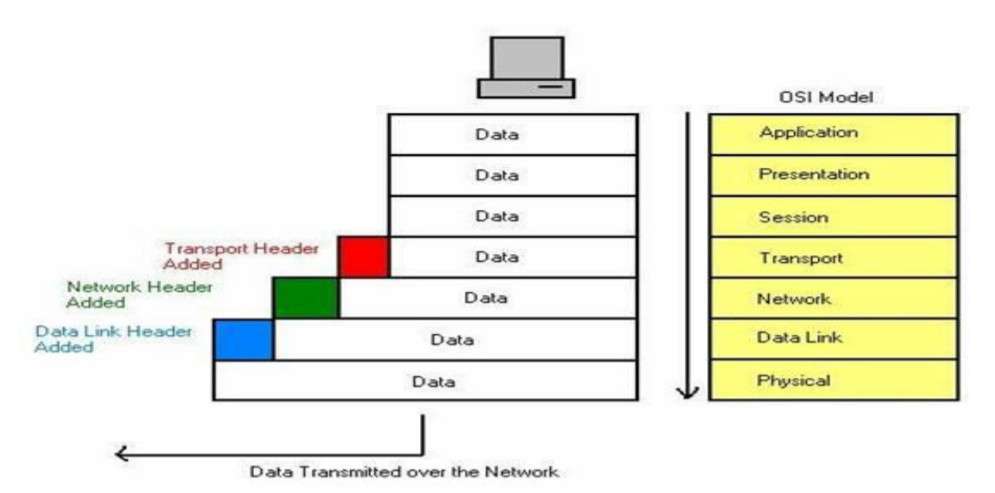
8. MAC address works on which layer? What are the differences of MAC sublayer and LLC sublayer?
MAC works at DATA LINK LAYER. Media Access Control provides physical addressing while Logical
Link Control provides error detection, using Ethernet trailer field frame check sequence (FCS). It is 4 bytes field. When a sending device sends a data it put the data in a mathematical algorithm and it gets a product, sending device puts the product in FCS. When a receiving device receive a data it also put the data in same mathematical algorithm and get a product. If both products are same, Frame is accepted or else discarded.
9. Which layer is responsible for converting data packets from the Data Link layer into electrical signals?
Physical Layer
10. At which layer is routing implemented, enabling connections and path selection between two end systems?
Network Layer
11. Which layer defines how data is formatted, presented, encoded,and converted for use on the network?
Presentation Layer
12. Which layer is responsible for creating, managing and terminating sessions between applications?
Session Layer
13. DNS uses which protocol? Why?
DNS uses both TCP and UDP. It is necessary to maintain a consistent DNS database between DNS Servers This is achieved by the TCP protocol. A client computer will always send a DNS Query using UDP Protocol over Port 53. If a client computer does not get response from a DNS Server, it must retransmit the DNS Query using the TCP after 3-5 seconds of interval.
14. Which layer is closer to the user?
From sender point of view, Application Layer is closest and from Receiver point of view Pgysical Layer is closest.
15. Differentiate between forward lookup and reverse lookup in DNS?
– Forward Lookup: Name to IP resolution
– Reverse Lookup: IP to Name resolution;
16. What is IPSec?
IPSec provides data security at the IP Packet Level.
17. What is the way to establish a TCP connection?
TCP Connection is established using three-way Handshake.
18. What is the difference between flow control and error control?
Error Controls the process of detecting and correcting both the bit and packet level error. While flow control is a mechanism to ensure the efficient delivery of Data. Flow control is agreeing on the minimum amount of data that a receiver can handle at a time.
19. What is RIP?
RIP is a Distance-Vector Routing protocol. It is a Classful routing protocol (Classful routing protocols do not send subnet mask information with their routing updates). It does not support VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masking). RIP uses Hop count as its metric to determine the best path to a remote network and it supports maximum hop count of 15. Any router farther than 15 hops away is considered as unreachable. It sends its complete routing table out of all active interfaces every 30 seconds.
20. What is route poisoning?
With route poisoning, when a distance vector routing protocol notices that a route is no longer valid, the route is advertised with an infinite metric, signifying that the route is bad. In RIP, a metric of 16 is used to signify infinity.
21. What is Split Horizon?
The Split Horizon feature prevents a route learned on one interface from being advertised back out of that same interface.
22. Utilizing RIP, what is the limit when it comes to number of hops?
Routing information protocol is one of the oldest distance vector routing protocols which employ the hop count as a routing metric.The maximum number of hops allowed for RIP is 15, which limits the size of networks that RIP can support.
23. Which category is RIP belong to?
RIP is a standard based, Distance Vector, Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) used by router to exchange the routing information.
24. Why is RIP known as Distance Vector?
RIP is known as Routing Information Protocol an it is a Distance Vector because it uses hop count to determine the best path to remote network. It has two version 1 (Classful) and version 2 ( Classless).
25. What is administrative distance of RIP?
Administrative distance of RIP is 120
26. Which metric is used by RIP?
Only Hop Count metric is used by RIP
27. What is the limit of hop count in RIP?
Limit of hop count in RIP is 15, mean if anything require 16 hop is deemed unreachable.
28. How is RIP select the best path to the remote network?
RIP only uses hop count to determine the best path to the remote network, route with lowest hop count will be prefer as best path to remote network. If RIP finds more than one link with the same hop count to the same remote network, it will automatically perform a Round-Robin load balancing. RIP can perform load balancing for up to 6 equal cost link and by default is 4.
29. Why RIP causes overhead in network?
Routers which are configured with RIP, periodically exchange all of its routing table information with others in every 30 seconds. So if assuming a scenario has 100 RIP networks in one router and there are 15 routers , so there would be 15 routers exchanging the information with each other even if its same info. Therefore, it causes overhead. If its RIPv1- then it will broadcast so every other router will hear the info. For RIPv2 its multicast
30. Which transport layer protocol used by RIP?
RIP use UDP (User Datagram Protocol) as one of its Transport protocol, and assigned the reserved port number 520.
