- CCNA Interview Questions [1]
- CCNA Interview Questions [2]
- CCNA Interview Questions [3]
- CCNA Interview Questions [4]
- CCNA Interview Questions [5]
- CCNA Interview Questions [6]
- CCNA Interview Questions [7]
- CCNA Interview Questions[8]
- CCNA Interview Questions [9]
- CCNA Interview Questions [10]
- CCNA Interview Questions [11]
- CCNA Interview Questions [12]
- CCNA Interview Questions [13]
- CCNA Interview Questions [14]
- CCNA Interview Questions [15]
- CCNA Interview Questions [16]

Top CCNA Interview Questions and Answers -2
1. Explain difference between Router,Switch and Hub?
Following are the differences in Hub, Routers and Switches :
Hubs
– Hubs operate at Layer 1 of OSI model.
– Hubs cannot process layer-2 or layer-3 traffic. Layer-2 deals with hardware addresses and layer-3 deals with logical (IP) addresses. So, hubs cannot process information based on MAC or IP addresses.
– Hubs cannot even process data based on whether it is a unicast, broadcast or multi-cast data.
– Hub transfers data to every port excluding the port from where data was generated.
– Hubs work only in half duplex mode.
– Collisions can happen.
– In case of a collision, a hub rejects data from all the devices and signals them to send data again. Usually devices follow a random timer after which data is sent again to hub.
– Maximum 2-12 number of ports can be found on Hubs.
Switches
– Switches are network devices that operate on layer-2 of OSI model. Some switches operate at higher level too.
– Switches are also known as intelligent hubs.
– Switches operate on hardware addresses (MAC) to transfer data across devices connected to them.
– It performs broadcast at first, after that Unicast.
– Major difference between Bridge and Switch being that a switch forwards data at wire speed as it uses special hardware circuits known as ASICs.
– Switches support full duplex data transfer communication.
– As layer 2 protocols headers have no information about network of data packet so switches cannot forward data based or networks and that is the reason switches cannot be used with large networks that are divided in sub networks.
– Switches can avoid loops through the use of spanning tree protocol.
– Switches can have 24-48 ports and can be practically unlimited ports because they don’t divide speed unlike Hubs.
Routers
– Routers are the network devices that operate at Layer-3 of OSI model.
– As layer-3 protocols have access to logical address (IP addresses) so routers have the capability to forward data across networks.
– Routers are far more feature rich as compared to switches.
– Routers maintain routing table for data forwarding.
– Routers have lesser port densities as compared to switches.
– Routers are usually used as a forwarding network elements in Wide Area Networks.
2. What is the difference between OSI and TCP/IP Model?

3. What is the size of IP Address?
The size of ipv4=32bit or 4byte and ipv6=128bit or 16bytes.
4. What is the range of class C address?
192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 Supports 254 hosts
5. What is POE (Power over Ethernet)?
Power over Ethernet or PoE pass electric power along with data on twisted pair Ethernet cabling. This allows a single cable to provide both data connection and electric power to devices such as wireless access points, IP cameras, and VoIP phones. It minimizes the number of wires required to install the network.
6. What are the advantages of Distributed Processing?
Distributed data processing is a computer-networking method in which multiple computers across different locations share computer-processing capability. This is in contrast to a single, centralized server managing and providing processing capability to all connected systems. Computers that comprise the distributed data-processing network are located at different locations but interconnected by means of wireless or satellite
Advantage: Lower cost, reliability, improved performance, reduced processing time, flexibility are the advantages of Distributed processing.
7. When were OSI model developed and why its standard called 802.XX and so on?
OSI model was developed in February1980 that why these also known as802.XX Standard 80 means =1980 & 2means =February
8. What is Full form of AD?
Administrative Distance or it can be Advertised Distance.
9. What is a peer-peer process?
Stands for “Peer to Peer.” In a P2P network, the “peers” are computer systems which are connected to each other via the Internet. Files can be shared directly between systems on the network without the need of a central server. In other words, each computer on a P2P network becomes a file server as well as a client.
10. What is ping? Why you use ping?
Ping is a utility used to test the connectivity in the network. It stands for Packet Internet Groper.it uses ICMP [internet Control message protocol ]Protocol.
11. Explain difference between straight and crossover cable with examples?
Straight cable is used to connect two different layer devices like router-switch, router-pc, and switch-pc while cross cable is used to connect two same layer devices like router-router, switch switch, and pc-pc. Color coding for both cable is different. If color coding on both ends of the cable is same, it is a straight cable, while if 1<–>3, 2<–>6 is being used, it is a cross cable for data transfer.
12. What is the difference between tracert and trace route?
Both Tracert and traceroute commands do similar purpose. On a router or switch you would use the command traceroute and on a pc you would use tracert.
Trace-route:
– You can find this utility in LINUX/UNIX based operating Systems.
– It rely over UDP Probe packet with destination PORT : 33434.
– It uses random Source PORT.
Tracert:
– You can find this utility in Windows based operating systems as well as Servers.
– It rely over ICMP Type 8(Echo Packet) & Type 0(Echo Request).
13. What is Round Trip Time?
Round-trip time (RTT), also called round-trip delay, is the time required for a packet to travel from a specific source to a specific destination and back again.Source is the computer sending the packet and the destination is a remote computer or system that receives the packet and retransmits it. A user can determine the RTT to and from an IP address by pinging that address.
14. Define the terms Unicasting, Multicasting and Broadcasting and Any-casting?
Unicasting means “one on one” communication, Multicasting means “one to many” communication but there must be atleast one devices that is not receiving the traffic while broadcasting means “one to all” communication. Each device receives packets in case of broadcasting. Anycast works in IPv6 and it means to “one to nearest” communication.
15. How many pins do serial ports of routers have?
In computer it’s known as com port and could be available in 9pin or 25 pin. On router it have 60 pins.
16. What are the differences between static ip addressing and dynamic ip addressing?
When a device is assigned a static IP address, the address does not change. Most devices use dynamic IP addresses, which are assigned by the network when they connect and change over time.
17. Difference between CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA?
CSMA/CD is responsible for detecting collision in wired media mainly, while CSMA/CA works on wireless media to completely avoid collision because detecting collision in wireless media is a bit hard.
18. What is DHCP scope?
A DHCP scope is a valid range of IP addresses that are available for assignment or lease to client computers on a particular subnet. In a DHCP server, a scope is configured to determine the address pool of IPs that the server can provide to DHCP clients. Scopes determine which IP addresses are provided to the clients.
19. What are the different memories used in a CISCO router?
– ROM
ROM is read-only memory available on a router’s processor board. The initial bootstrap software that runs on a Cisco router is usually stored in ROM. ROM also maintains instructions for Power-on Self Test (POST) diagnostics.
– Flash Memory
Flash memory is an Electronically Erasable and Re-Programmable memory chip. The Flash memory contains the full Operating System Image (IOS, Internetwork Operating System).Flash memory retains content when router is powered down or restarted.
– RAM
RAM is very fast memory that loses its information when the router is shutdown or restarted. On a router, RAM is used to hold running Cisco IOS Operating System, IOS system tables and buffers RAM is also used to store routing tables,RAM Provides temporary memory for the router configuration file of the router while the router is powered on.
RAM Stores running Cisco IOS Operating System, Active program and operating system instructions, the Running Configuration File, ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) cache, routing tables and buffered IP Packets.
– NVRAM (Non-volatile Random Access Memory)
NVRAM is used to store the Startup Configuration File. This is the configuration file that IOS reads when the router boots up. It is extremely fast memory and retains its content when the router is restarted.
20. What are the different types of passwords used in securing a CISCO router?
Enable password, Secret Password, Line passwords (VTY, Console and Aux) are the passwords used in Router.
21. What are the different types of passwords used in securing a CISCO router?
Depending on Connection (Device) :
– Enable password
– Console password
– VTY password
– AUX password
22. What is the use of “Service Password Encryption”?
Service Password Encryption command encrypts plain text password into type 7 password. These are not very much secure and can be easily decrypted.
23. What is DLCI?
A data link connection identifier (DLCI) is a Frame Relay 10-bit-wide link-local virtual circuit identifier used to assign frames to a specific PVC or SVC. Frame Relay networks use DLCIs to statistically multiplex frames. DLCIs are preloaded into each switch and act as road signs to the traveling frames.
24. Briefly explain the conversion steps in data encapsulation?
Process of adding header and trailer information in data is called Data Encapsulation. Whenever a layer passes the data to next layer it adds some extra information in data. This is called header. Next layer then processes the data and adds its own header. This process continues until data is place on physical media. This process is called Encapsulation. Removing header and trailer information from the data is called Data Decapsulation.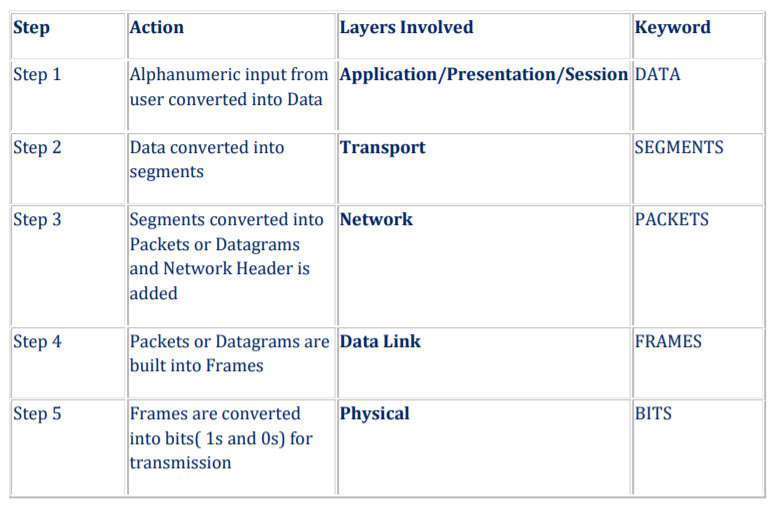
25. In configuring a router, what command must be used if you want to delete the configuration data that is stored in the NVRAM?
Erase startup-config is the command to delete preconfigured files on the router.
26. IEEE standard for wireless networking?
802.11
27. What is the range of class A address?
From 0.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255, but we cannot use 0 and 127, so actual range is from 1 to 127
28. What is the range of class B address?
From 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255
29. Differentiate Logical Topology from Physical Topology?
Physical topology represents the physical structure i.e cabling of the network while logical topology deals with the data flow in the network.
30. What is AS (Autonomous System)?
A group of devices under a single administration is called an AS. AS Number is assigned by IANA (The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority)
